Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain. It’s primarily used to treat depression, especially in cases where traditional treatments such as medication and therapy have not been effective.
How Does TMS Work?
TMS involves placing a magnetic coil on the scalp, which sends magnetic pulses through the skull to specific areas of the brain. These pulses create small electrical currents that can either increase or decrease the activity of brain cells in those regions. The procedure doesn’t require anesthesia, and patients can go about their day immediately after each session.
During a typical session, which lasts about 20 to 40 minutes, patients sit comfortably while the magnetic coil is positioned over the targeted area. This area is usually the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain which is linked to mood regulation.
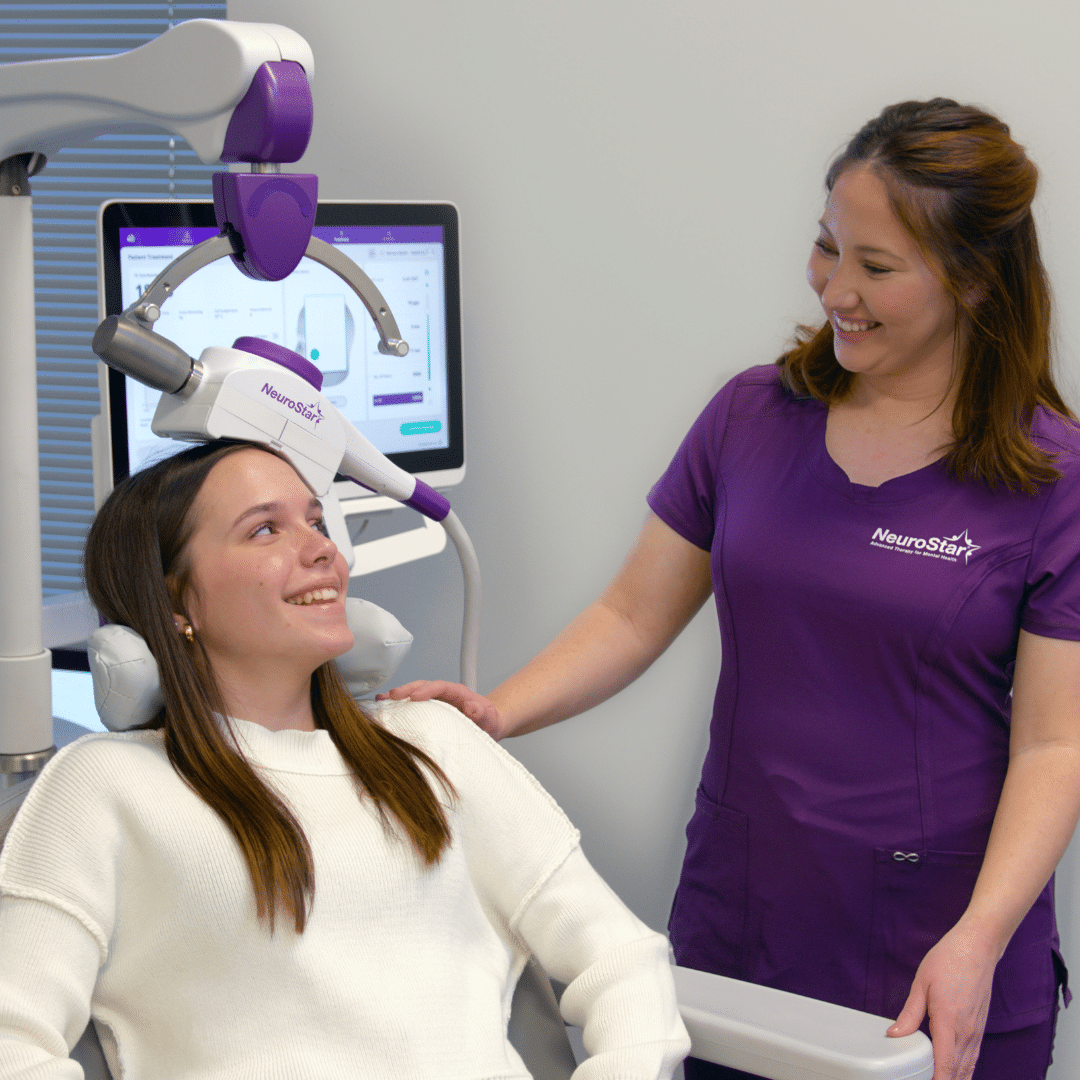
What Happens to Your Brain During TMS?
TMS works by targeting the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain associated with mood regulation. The magnetic pulses induce electrical currents that can either increase or decrease neuronal activity in this area, depending on the settings used. This modulation of brain activity can help alleviate symptoms of depression by normalizing the function of neural circuits that are dysregulated in mental health conditions.
During the treatment, patients may feel a tapping sensation on their scalp and hear a clicking noise from the magnetic coil. These sensations are generally well-tolerated and become less noticeable over time.
TMS Therapy Benefits
Effective for Treatment-Resistant Depression

One of the biggest advantages of TMS is its effectiveness for people with major depressive disorder who haven’t responded to conventional treatments. Studies show that between 50% and 60% of these individuals experience significant improvement in their symptoms after TMS therapy.
Non-Invasive and Convenient
Unlike other treatments such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), TMS does not require general anesthesia and can be performed on an outpatient basis. This makes it a convenient option for many patients.
Expanding Applications
Beyond depression, TMS is being explored as a treatment for various other conditions, including anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and even chronic pain and migraines. Research on the effectiveness of TMS in the treatment of psychiatric disorders is ongoing, but initial results are promising.
Side Effects of TMS
While TMS is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects such as headaches, scalp discomfort, or lightheadedness. These side effects are usually mild and transient but can be bothersome for some individuals. There is also a very small risk of seizures associated with TMS, particularly in individuals with certain predisposing conditions. However, the incidence rate is about 0.1%, making it a rare complication.

Final Thoughts
TMS therapy offers a promising alternative for individuals with treatment-resistant depression and other mental health conditions. Its non-invasive nature and potential efficacy make it an attractive option. However, as with any medical treatment, it is essential to weigh the benefits against potential downsides and consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. Visit our TMS treatment page for more information or contact our team if you would like to inquire about TMS therapy.
Responsibly edited by AI
Other Blog Posts in
Animo Sano Psychiatry is open for patients in North Carolina, Georgia and Tennessee. If you’d like to schedule an appointment, please contact us.
Get Access to Behavioral Health Care
Let’s take your first step towards. Press the button to get started. We’ll be back to you as soon as possible.ecovery, together.