Breaking the Cycle: The Impact of Parental Mental Health on Children’s Behavior
Maddison Henley PA-C

Parental mental health significantly influences children’s behavior and emotional development. Studies reveal that parents who struggle with mental health issues—such as anxiety, depression, or trauma—may inadvertently influence their child’s behavior, creating patterns that are often challenging to break. Understanding this connection is crucial for fostering healthier family dynamics and promoting positive outcomes for children.
The Influence of Parental Mental Health on Children
Children are highly perceptive and often mirror their parents’ emotional states. When parents experience mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, or trauma, these issues can manifest in their children’s behavior. For instance, a study published found that children of parents with depression are more likely to exhibit behavioral problems and emotional difficulties.
Parental mental health can affect parenting styles, leading to inconsistent discipline, emotional unavailability, or overprotectiveness. These behaviors may contribute to children’s development of anxiety, depression, or behavioral disorders. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that children with parents who have mental health issues are at a higher risk of developing similar problems themselves.
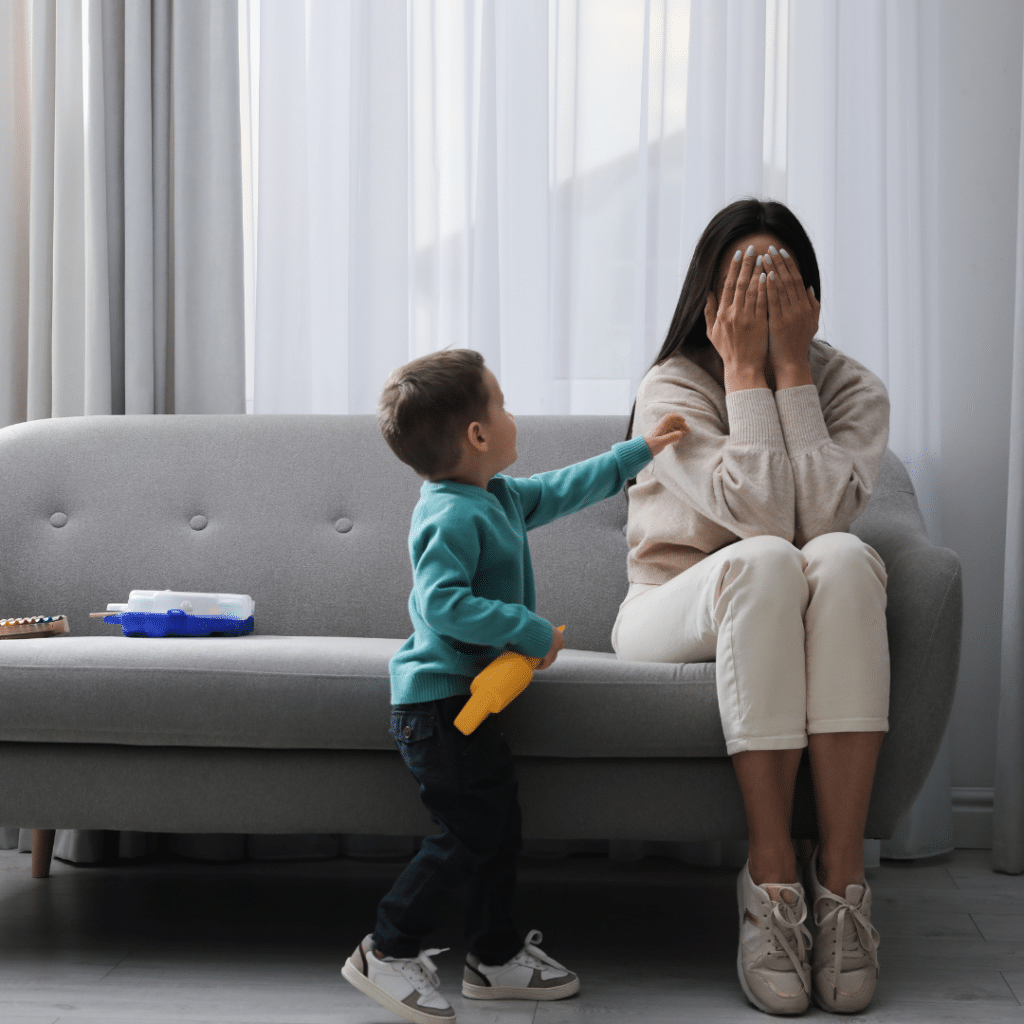

Intergenerational Transmission of Trauma
Trauma can be passed from one generation to the next, a phenomenon known as intergenerational transmission of trauma. This occurs when parents who have experienced trauma inadvertently influence their children’s emotional well-being. According to Psychology Today, children of parents with unresolved trauma may exhibit symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and behavioral issues.
The mechanisms behind this transmission include genetic factors, parenting behaviors, and environmental influences. For example, a parent who has experienced trauma may have difficulty regulating emotions, leading to a stressful home environment that affects the child’s development. A study in the Journal of Health Service Psychology highlights the importance of addressing parental trauma to prevent its transmission to children.
Breaking the Cycle
Understanding the link between parental mental health and children’s behavior is the first step in breaking unhealthy patterns. Here are actionable steps parents can take:
- Acknowledge the Issue: Recognizing that mental health challenges exist is a powerful step forward. Research indicates that parents who acknowledge their struggles are more likely to seek help, benefiting their children.
- Seek Professional Support: Therapy and counseling can provide parents with tools to manage mental health symptoms. Professional support can provide coping strategies and emotional regulation techniques, benefiting both the parent and the child. The American Psychological Association (APA) emphasizes the importance of mental health treatment for parents to improve family dynamics.
- Foster Open Communication: Talking openly about emotions helps children feel secure and understood. Research emphasizes that families with open lines of communication have children who exhibit fewer behavioral problems.
4. Model Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Parents who demonstrate effective ways to manage stress—like mindfulness, exercise, or journaling—teach children resilience. For example, a study in Frontiers in Psychology found that children whose parents practice mindfulness are 25% less likely to develop anxiety.
5. Create a Supportive Environment: Establishing a stable and nurturing home environment can help children feel secure and valued. Consistency in routines, positive reinforcement, and emotional support are key components. The CDC highlights the role of a supportive family environment in promoting children’s mental health.
Final Thoughts
Parental mental health profoundly impacts children’s behavior and emotional development. By acknowledging and addressing their mental health challenges, parents can create a positive environment that fosters healthy development for their children. Implementing strategies such as seeking professional support, fostering open communication, modeling healthy behaviors, and creating a supportive environment can help break the cycle of negative behavioral patterns and promote well-being for both parents and children.
Responsibly edited by AI
Other Blog Posts in
Animo Sano Psychiatry is open for patients in North Carolina, Georgia and Tennessee. If you’d like to schedule an appointment, please contact us.
Get Access to Behavioral Health Care
Let’s take your first step towards. Press the button to get started. We’ll be back to you as soon as possible.ecovery, together.




